Elements of a Database
There are four main elements, called objects of an Access database. Here they are in brief.
- Table
-
A set of data entries (records) whose model is defined by a set of columns (fields). A table has a predefined number of columns, but can have any number of rows.
- Form
-
A user-interface designed for entering data into a table or tables. It presents this interface so that the database designer does not have to worry about the end users messing up the database tables.
- Query
-
A tool for searching the database. Parameters are defined for the search and the user can filter the table or tables in a variety of different ways.
- Report
-
A report is a database tool which allows the user to pull well-formatted data. It offers the ability to print your data in a way that is readable and understandable.
Tables
In a spreadsheet, columns and rows are flexible. They can mean anything you like. In a database, however, rows and columns have very specific purposes. In all database software, a column is called a field and a row is called a record. So a row in the veterinarian's Customer table would be one customer's contact data. His or her name, phone number, address, billing information, and a list of pets.
Each column in a database comes with a type. This is specified when the table is created and cannot be changed -- well, not without extreme difficulty. These data types can be anything from strings of text, to numbers, to special binary types called booleans. Recall the customer table from the previous section. Here is a more detailed version of that table:
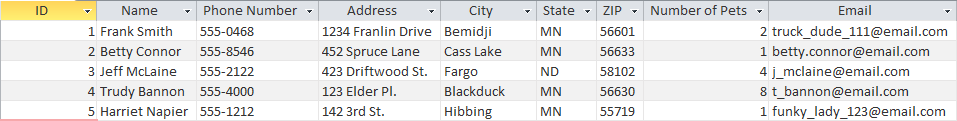
What kind of data do you think each field in this table represents?
Forms
Access has a user-interface which you will use to create and modify a database. But as the database administrator, the absolute last thing you want anyone else to have is direct access to your database, its fields, or its contents. So Access has a way for you to create your own user interfaces so that your employees or co-workers can have a nice, clean interface where they can't mess anything up.
Here is what a customer information form might look like:
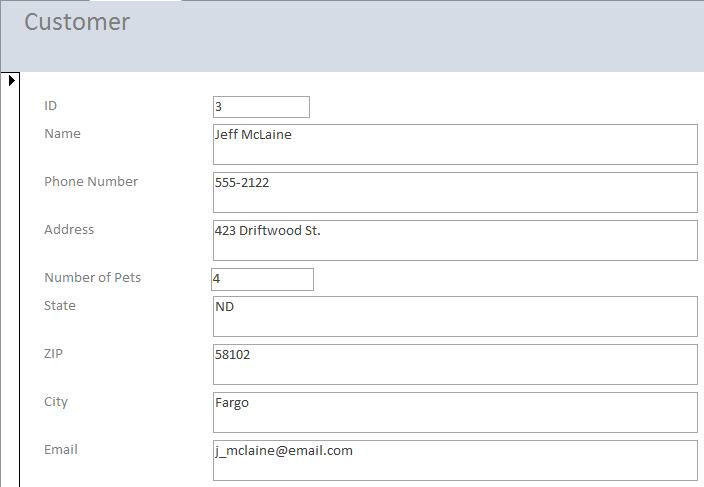
From this basic design, the form can be customized, themed, and tweaked almost infinitely.
Forms even allow you to enter data into multiple tables at once! They are a powerful tool that give you the power to decide how your database grows, how its entered, and what happens to it once it is.
Queries
A database engine is only as good as its ability to search a dataset. Thus, one of your most important tools in database management is the query. With a query, you build a set of parameters involving one, two, or many of your database tables which the software will then use to search the database and generate a result. Perhaps you want to see the list of all of the pets owned by a particular customer. That's what a query is for.
This might be the result of a query that searches for all of the pets owned by a particular customer:
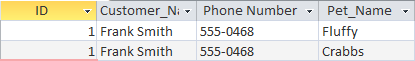
Reports
A report is document which can be generated at will which organizes your data in ways that are more readable. They are designed to be printable or exported to a PDF. This is how you might create copies of information for a meeting or for filing purposes. You can build reports straight from a table, or from a query, which gives you incredible control over how your information is displayed to whoever reads your reports. Here is a report generated from the above query:
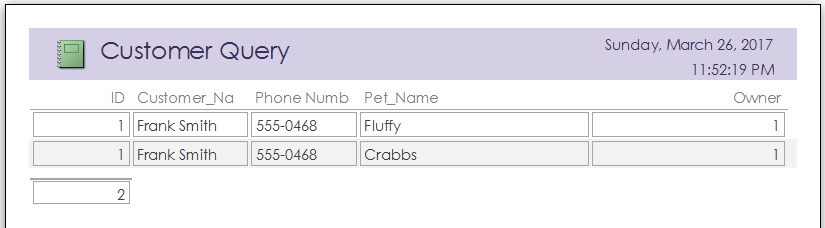
Making sense of it all
These four objects have a complex relationship with each other, however, with a little practice, you'll be an expert in database fundamentals. The table is the most fundamental aspect of the database and every piece of information in the database must come from one table or other originally. Here is a breakdown of the relationship between the four components of a database:
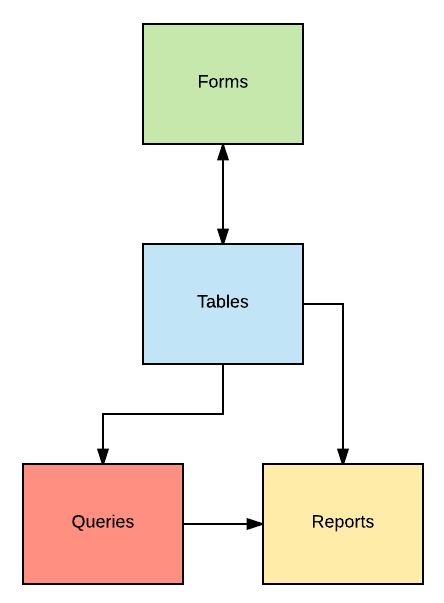
It breaks down kind of like this: * Tables generate Forms and Forms modify individual records in tables. * Queries search one or more tables Tables for specific data. * Reports format Table data or Query results for printing.
As we continue on, you will see many of the ways in which these powerful tools can be used to build ways to maintain, organize, and search datasets. Pace yourself and don't give up. It will make sense in the end.